Introduction
SEM, or Search Engine Marketing, includes two channels – SEA, also known as PPC or paid search; and SEO for free organic traffic. The two digital marketing channels are among the most important ones for any online business.
According to YOAST, in 2021 organic search drove 53% of website traffic, while paid search drove 27%. This means together the two SEM channels make 80% of internet traffic!
Each channel has its tactics, use cases, and pros and cons, plus a huge community of marketers that swear that their channel brings more value to businesses.
However, SEA and SEO aren’t rivaling channels. They actually complete one another.
In this article, I’ll go over the characteristics and use cases of each channel, and how digital marketers can use them together to grow their businesses.
- Introduction
- What Is SEO?
- What Is SEA (PPC)?
- What Are The Benefits of SEO?
- What Are The Disadvantages of SEO?
- What Are The Benefits of Google Ads?
- What Are The Disadvantages of Google Ads?
- When Should I Use SEO?
- When Should I Use Google Ads?
- Which is better – SEA or SEO?
- Creating synergies between SEO and SEA
- Conclusion
- Further Reading:
- FAQs:
What Is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization and is synonymous with organic search. The term search engines refers to all of them – Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc… Although most of the focus goes to Google, with its giant market share of 85%.
The goal of SEO is to increase organic traffic to a website. This means, traffic that clicks a free link from a search engine results page (SERP).
SEO marketers use certain tactics to improve how their website ranks on Google or Bing to relevant search queries. The better their rankings, and the more relevant keywords they rank for, the more organic traffic they’ll get for their website.
SEO can be divided into three main sub-topics – content SEO, technical SEO, and off-page SEO.

What is Content SEO?
Content SEO covers the content aspects of a certain webpage, including the URL, headlines, text, images, and more.
To improve the ranking of a certain webpage to a keyword, SEOs must send Google as many signals as possible that their page is the most relevant for any user researching that keyword on Google.
When a website creates many blog articles to target relevant keywords around a certain topic, that’s an example of content SEO. Creating these new articles will help the website to rank for more keywords. By that, it will reach more potential customers and increase its organic traffic.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO covers other, more technical aspects. These include crawlability (Google bot can read and crawl the page), having a good sitemap, page load speed (the faster the better), providing a good user experience (accessibility, site responsiveness, not having too many pop-ups), not having broken links (404s), having a schema markup in place and more.
Even if the content on a page is very good and comprehensive, having poor technical SEO will impact its chances to rank well on Google.
What Is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken off your website, for example, building backlinks and getting mentions on other sites.
Backlinks are links to your content from other websites. They are an important ranking factor – the more backlinks you have, and the better their quality, the better the chances of your content ranking high on Google.
Other tactics of off-page SEO with indirect impact include social media, PR, events, podcasts, etc. The idea is that each of these channels creates more opportunities for backlinks and organic traffic to your website.
What Is SEA (PPC)?
SEA stands for Search Engine Advertising and is also known as PPC (Pay Per Click) or Paid Search.
The biggest PPC advertising platform is by far Google Ads, followed by Bing Ads. Throughout this article, I’ll be using SEA, PPC, and Google Ads interchangeably.
PPC marketers use Google Ads to bring potential customers to their websites by bidding on relevant keywords. This means they can show relevant ads exactly when a potential customer is searching for something on Google.
Being able to serve ads to potential customers with high intent often generates good results, such as a lead for a B2B business or a purchase for an online store.
Google Ads offers a wide range of ad formats and placements, e.g. text, shopping, display, video, app downloads, and even Gmail ads. In most cases, advertisers only have to pay when a user clicks on their ads.
Let’s move on to discuss the pros and cons of SEO and SEA.
What Are The Benefits of SEO?
SEO is one of the biggest digital marketing channels for a reason. Some of its benefits are:
- Free traffic!!!
- SEOs can create content to target all funnel stages
- Helps to create brand authority and trust
- Potential customers trust organic results more than ads, which can translate to higher conversion rates
- Organic results on the SERP aren’t blocked by any ad blockers
- Long-term results: Once good content is created, it will generate traffic for a long period with little maintenance and strong ROI
What Are The Disadvantages of SEO?
Even with its huge benefits, SEO has its limitations. Some of the disadvantages of SEO are:
- Good content takes time, effort, and expertise to create
- Great content won’t rank by itself. Building backlinks can be just as hard as executing a content strategy
- Results take time to show, often 6-12 months after creating the content
- SEO rankings may be impacted by Google’s core algorithm updates

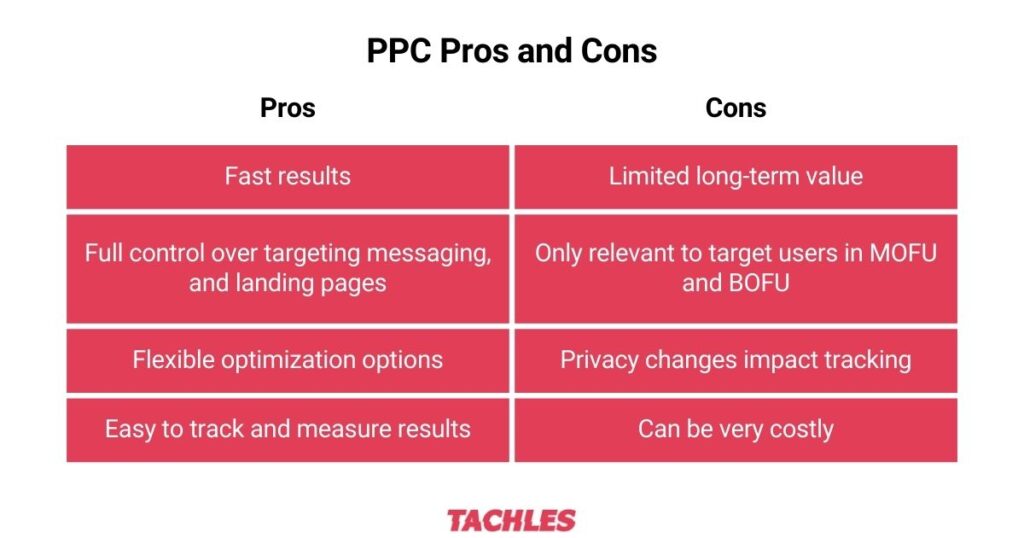
What Are The Benefits of Google Ads?
Google Ads has many benefits as well, including:
- Full control over targeting, messaging, and landing pages
- Fast results
- Easy to track and measure results
- Flexible optimization options – can target new keywords, increase budgets, etc…
What Are The Disadvantages of Google Ads?
Google Ads is a great PPC platform to catch existing demand, but also has some limitations:
- Can be very costly and CPCs only increase over time
- Privacy restrictions make tracking and attribution harder
- Search and Shopping campaigns are only relevant to target users in the middle and bottom funnel stages
- Limited long-term value: Once an advertiser stops paying for ads, traffic to their website will decrease.
When Should I Use SEO?
SEO should be an essential part of any online marketing strategy. You should make sure that all relevant pages on your website are optimized to rank high on search engines.
SEO is great to compensate for two of the main issues paid search has – its limited reach to prospects in the high funnel stages, and the high CPC bids some competitive keywords have.
Example 1 – Ecommerce store for rugs:
- Make sure your modern rug collection page includes ‘modern-rugs’ in the URL as well as in the H1 title, meta title, and meta description.
- Make sure your product page for ‘Wool Rug Alex’ includes ‘wool rug’ in the URL, H1, meta title, and meta description.
- Make sure you create blog articles based on keyword research to reach potential customers
Example 2 – Website of a B2B SaaS company offering online analytics:
- Create blog articles to target potential customers in all funnel stages:
- TOFU – Create content about different online channels – Google Ads, Facebook Ads, CRM, SEO
- MOFU – Create content about tracking, attribution, and analytics
- BOFU – Create content showing how your solution solves problems online marketers experience and adds value to their daily tasks
Once your content is created and starts to rank, it should generate organic traffic with very low maintenance for a relatively long period.
Click here to read about common SEO mistakes you should avoid.
When Should I Use Google Ads?
PPC campaigns on Google Ads are great to achieve results fast. As long as the campaigns drive a positive ROI, there’s no real reason to pause them.
Paid search campaigns are also essential in order to serve ads for keywords your website doesn’t rank high enough for.
Let’s say for example your average organic ranking for the keyword ‘rugs’ is 12. This means without a Google Ads campaign bidding on that word, your website will get very few clicks for it.
For very competitive keywords with a high CPC, it might not be profitable to spend a lot on ads. In these cases, it might be worthwhile to target the competitive keyword with a blog article.
And even if you rank 1st on Google for your top 100 keywords – ads from your competitors, as well as other features on the SERP, might show above you. Think maps, knowledge boxes, etc…
Click here to learn how to create Google Search campaigns.
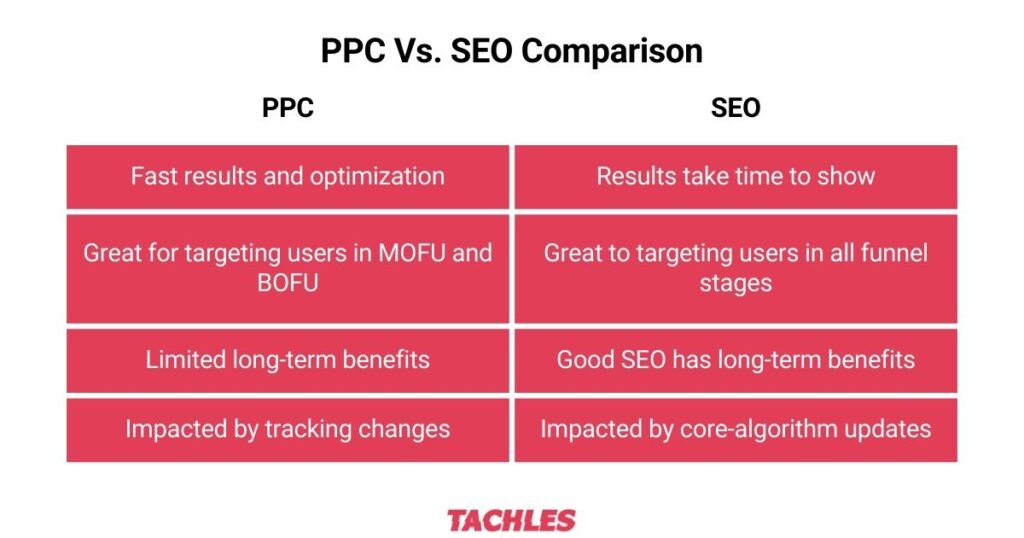
Which is better – SEA or SEO?
This debate among digital marketers is as old as Google. And the answer?
When done well, SEO can have an amazing ROI. A strong SEO performance is essential to maintain profitability in the long run.
In the ideal world, we’d get tons of free organic traffic. We’ll get so much traffic that we wouldn’t need to run SEA campaigns on Google Ads. Although this isn’t the case for 99% of online businesses.
Paid search plays an important role in their marketing strategy, allowing them to target keywords they don’t rank for organically. Brands that rely too heavily on PPC might struggle to protect their margins.
So which channel is better, paid or organic search? Neither. Both work together to help marketers meet business goals.
Creating synergies between SEO and SEA
Rather than look at SEO and SEA as two separate channels, marketers should adopt a holistic perspective, seeing them as complementary.
Here are a few examples of how search marketers can create synergies between paid and organic search:
- Popular tools for keyword research are used for both channels: Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, or SERanking.
- Review organic search terms in Google Search Console – are any of them relevant for a PPC campaign?
- Review paid search terms in Google Ads – should we set up new pages to target them with SEO (e.g. a new collection page or blog article)?
- Identify too-expensive keywords on Google Ads and optimize site content to target them organically
- Review organic rankings on Google Search Console to identify valuable keywords or pages that don’t rank high enough; Increase paid search traffic to these keywords or pages
You can link Google Ads and Google Search Console to identify opportunities.
Conclusion
While the debate between search marketers continues on which channel is better, PPC or SEO, taking a step back will help us to see the bigger picture.
Neither PPC nor SEO is better than the other. These are different channels that serve different objectives and often complete one another.
Search marketers who understand both channels will enjoy a power multiplier and a better chance of growing their business.
Further Reading:
- Google Ads vs. Facebook Ads For Ecommerce: Which Advertising Platform Is Better For Your Business?
- 13 Ways To Optimize Google Shopping Ads (In A Profitable Way)
- Automation Magic: Enhance Results with Responsive Display Ads
- How to Create Powerful Dynamic Remarketing Ads on Google
- Google Dynamic Search Ads: A Great Way to Boost Your Online Sales
FAQs:
Which is better – organic or paid search?
SEO and PPC are both used to get clicks from potential customers on the SERP. Having good organic rankings is important in the long run, but PPC is essential in order to generate revenues in the short term. Paid search is also essential to prevent ads from competitors to steal your organic traffic.
Do Google Ads help with SEO?
While Google doesn’t mention Google Ads as an SEO ranking factor, many digital marketers believe there is an indirect effect.
When prospects see your ads repeatedly, an unconscious familiarity effect increases the chances that they’ll eventually click on an organic result.
And the more organic clicks you get, the better your rankings will become.
What’s the difference between SEO and PPC?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. The meaning of SEO is using certain tactics to improve organic rankings on Google’s SERP, which would translate into free traffic.
PPC stands for Pay Per Click. It’s synonymous with SEA (Search Engine Optimization) and paid search. The biggest PPC channel is by far Google Ads. Here, advertisers bid on keywords, or products, to show ads to potential customers on the SERP, above the organic results.
What’s the difference between SEM, SEA, and SEO?
SEM stands for Search Engine Marketing. This term includes both SEA for paid search and SEO for organic search.

